Tigers are one of the most majestic and powerful creatures on the planet, but where do tigers live habitat? Understanding their natural habitat is crucial for their conservation and survival. The tiger's habitat is as diverse as the species itself, ranging from dense forests to grasslands and even mangroves. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the intricacies of their habitats and the challenges they face in today's world.
Tigers are not just symbols of strength and beauty; they are also critical components of the ecosystems they inhabit. Their presence in a habitat signifies a healthy environment, as they play a vital role in maintaining the balance of nature. However, due to human activities such as deforestation and poaching, the natural habitats of tigers are under threat, making conservation efforts more important than ever.
In this article, we will explore the various habitats where tigers live, the factors that influence their distribution, and the conservation efforts aimed at protecting these magnificent animals. By the end of this piece, you will have a deeper understanding of the tiger's habitat and the urgent need to preserve it.
Read also:Air Element Signs Understanding The Traits Characteristics And Compatibility
Table of Contents
- Biological Overview of Tigers
- Primary Habitat Types for Tigers
- Sub-Tropical Forests: A Haven for Tigers
- Tropical Rainforests: The Dense Jungles
- Mangrove Forests: The Unique Wetland Habitat
- Threats to Tiger Habitats
- Conservation Efforts for Tiger Habitats
- Human-Tiger Conflict and Its Impact
- Global Initiatives for Tiger Conservation
- Future Prospects for Tiger Habitats
Biological Overview of Tigers
Tigers (Panthera tigris) belong to the Felidae family and are one of the largest carnivorous mammals on Earth. They are apex predators, meaning they sit at the top of the food chain in their ecosystems. There are six recognized subspecies of tigers: Bengal, Siberian, Indochinese, Malayan, Sumatran, and South China tigers. Each subspecies has adapted to its unique environment, which influences its behavior, diet, and physical characteristics.
Key biological facts:
- Tigers can weigh between 220 to 660 pounds, depending on the subspecies.
- They have a lifespan of 10-15 years in the wild and up to 20 years in captivity.
- Tigers are solitary animals, with each individual maintaining a large territory.
- They are excellent swimmers and can cover long distances in water.
Understanding the biology of tigers is essential for comprehending their habitat requirements. For instance, their need for large territories means that their habitats must be vast and undisturbed to support their survival.
Primary Habitat Types for Tigers
The question of "where do tigers live habitat" can be answered by examining the primary habitat types they inhabit. Tigers are incredibly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, provided there is sufficient prey, water, and cover. The following are the main types of habitats where tigers live:
Sub-Tropical Forests: A Haven for Tigers
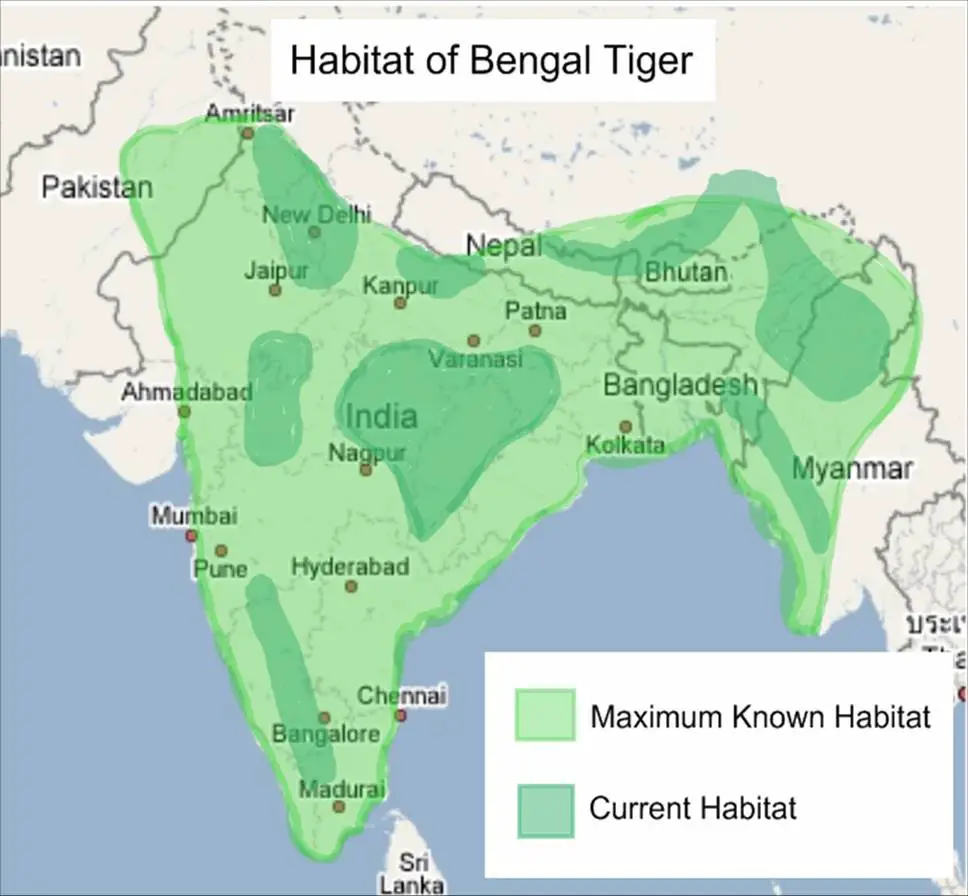
Sub-tropical forests, such as those found in India and Nepal, are one of the most common habitats for tigers. These forests are characterized by warm temperatures and moderate rainfall, making them ideal for the growth of dense vegetation. Tigers in sub-tropical forests rely on the cover provided by trees and shrubs to stalk their prey.
According to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), sub-tropical forests are home to the Bengal tiger, which is the most populous subspecies. The Sundarbans, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an example of a sub-tropical forest that supports a significant tiger population.
Read also:Conchita Martinez Compagnon A Closer Look At Her Life Career And Accomplishments
Tropical Rainforests: The Dense Jungles
Tropical rainforests are another important habitat for tigers, particularly in Southeast Asia. These forests are known for their high biodiversity and dense canopy, which provides ample cover for tigers. The Sumatran tiger, one of the smallest subspecies, is native to the tropical rainforests of Sumatra.
Research by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) shows that tropical rainforests are under severe threat due to deforestation and logging. This poses a significant risk to the survival of tigers in these regions.
Mangrove Forests: The Unique Wetland Habitat
Mangrove forests are a unique type of habitat that supports tiger populations in certain areas. The Sundarbans, located in Bangladesh and India, is the largest mangrove forest in the world and is home to the Bengal tiger. Mangroves provide a rich source of prey, such as fish and small mammals, and protect tigers from human interference.
However, climate change and rising sea levels are threatening the existence of mangrove forests, which could have devastating consequences for the tiger population in these areas.
Threats to Tiger Habitats
Despite their adaptability, tigers face numerous threats to their habitats. Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion have significantly reduced the available habitat for tigers. Additionally, poaching for their body parts and illegal wildlife trade continue to pose a major threat to their survival.
Key threats:
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture and development reduces the available space for tigers.
- Poaching: Tigers are hunted for their skin, bones, and other body parts, which are used in traditional medicine.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns affect the availability of prey and water sources.
Addressing these threats requires a concerted effort from governments, conservation organizations, and local communities to protect tiger habitats and ensure their long-term survival.
Conservation Efforts for Tiger Habitats
Conservation efforts for tiger habitats are crucial for reversing the decline in tiger populations. Various initiatives have been launched to protect tigers and their habitats, including the establishment of national parks, wildlife reserves, and corridors that connect fragmented habitats.
One notable initiative is Project Tiger, launched by the Indian government in 1973, which aims to conserve tigers and their habitats through scientific management and community involvement. Similarly, the Global Tiger Recovery Program (GTRP) is a collaborative effort between countries to double the wild tiger population by 2022.
Conservationists also emphasize the importance of involving local communities in conservation efforts. By providing alternative livelihoods and education, communities can become allies in protecting tiger habitats.
Human-Tiger Conflict and Its Impact
Human-tiger conflict is a significant issue in areas where tiger habitats overlap with human settlements. As human populations grow and expand into tiger territories, conflicts over resources and space become inevitable. Tigers may attack livestock or even humans, leading to retaliatory killings by local communities.
Solutions to human-tiger conflict:
- Creating buffer zones between tiger habitats and human settlements.
- Implementing compensation schemes for farmers who lose livestock to tigers.
- Using technology, such as camera traps and GPS collars, to monitor tiger movements and prevent conflicts.
Addressing human-tiger conflict is essential for ensuring the coexistence of humans and tigers in shared landscapes.
Global Initiatives for Tiger Conservation
Global initiatives play a critical role in tiger conservation by bringing together governments, organizations, and individuals to work towards a common goal. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) regulates the trade of tiger products to prevent illegal poaching. Similarly, the Tiger Conservation Partnership (TCP) supports countries in developing effective conservation strategies.
International organizations such as the WWF and Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) are actively involved in tiger conservation efforts. They conduct research, implement conservation programs, and raise awareness about the importance of protecting tiger habitats.
Future Prospects for Tiger Habitats
The future of tiger habitats depends on the success of conservation efforts and the willingness of governments and communities to protect these vital ecosystems. Advances in technology, such as remote sensing and satellite imagery, offer new opportunities for monitoring and managing tiger habitats more effectively.
Moreover, the growing awareness of the importance of biodiversity conservation among the global population provides hope for the future of tigers. By working together, we can ensure that tigers continue to thrive in their natural habitats for generations to come.
Kesimpulan
Where do tigers live habitat? The answer lies in the diverse ecosystems that support these magnificent creatures. From sub-tropical forests to mangroves, tigers have adapted to a wide range of environments. However, their habitats are under threat due to human activities and climate change, making conservation efforts more critical than ever.
We urge you to take action by supporting conservation organizations, spreading awareness about tiger conservation, and advocating for policies that protect tiger habitats. Together, we can ensure that tigers continue to roam the Earth in their natural glory.
Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with your friends and family to help spread the word about tiger conservation. Remember, every small action counts in the fight to save these incredible animals.