Tigers are among the most majestic and iconic animals in the world, but where does the tiger live? Understanding their habitats is crucial for their conservation and survival. These magnificent creatures once roamed vast territories across Asia, but today, their populations are under threat due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. This article explores the diverse environments where tigers thrive and highlights the importance of protecting their natural habitats.
As one of the largest big cats, tigers have adapted to a variety of ecosystems, from dense tropical rainforests to snowy boreal forests. However, the rapid expansion of human activities has significantly reduced their natural habitats. By understanding the specific regions where tigers live and the challenges they face, we can take meaningful steps to ensure their survival for future generations.
In this article, we will delve into the various habitats where tigers live, the factors affecting their survival, and the ongoing efforts to protect them. Whether you're a wildlife enthusiast, an environmentalist, or simply curious about these magnificent animals, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the world of tigers.
Read also:The Founder Ottoman Kpkuang Ndash Unveiling The Visionary Entrepreneur
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Tigers
- Primary Habitats Where Tigers Live
- Sub-Habitats: Exploring Specific Regions
- Tiger Species and Their Habitats
- Threats to Tiger Habitats
- Conservation Efforts for Tigers
- Impact of Climate Change on Tiger Habitats
- Role of Human Activities in Tiger Habitat Loss
- Interesting Facts About Tiger Habitats
- Conclusion
Introduction to Tigers
Tigers are apex predators that play a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Native to Asia, these big cats are known for their striking orange coats with black stripes and powerful build. Despite their adaptability, tigers are classified as endangered, with fewer than 4,000 individuals remaining in the wild. Their habitats are as diverse as the species themselves, ranging from tropical forests to grasslands.
Understanding where tigers live is essential for conservation efforts. By identifying the key regions where tigers thrive, scientists and conservationists can develop targeted strategies to protect these animals and their habitats. In the following sections, we will explore the primary habitats where tigers live and the factors that influence their distribution.
Primary Habitats Where Tigers Live
Tigers are adaptable creatures that can survive in a variety of environments. However, they prefer habitats that provide ample cover, prey, and water. The primary habitats where tigers live include:
- Tropical Rainforests: Dense forests with high rainfall, such as those in Southeast Asia, provide ideal conditions for tigers.
- Grasslands and Savannas: Open grasslands, particularly in India, offer tigers ample opportunities to hunt and roam.
- Deciduous Forests: These forests, found in regions like Nepal and Bhutan, provide seasonal cover and prey.
- Evergreen Forests: Evergreen forests, particularly in Myanmar and Thailand, support tiger populations year-round.
Sub-Habitats: Exploring Specific Regions
Within the primary habitats, tigers occupy specific sub-habitats that cater to their needs. For example:
- Terai Arc Landscape: Located in the foothills of the Himalayas, this region supports a significant tiger population.
- Sunderbans: The world's largest mangrove forest, located in India and Bangladesh, is home to the Bengal tiger.
- Amur-Heilong: The boreal forests of Russia's Far East provide a unique habitat for the Siberian tiger.
Tiger Species and Their Habitats
There are six recognized subspecies of tigers, each adapted to specific habitats:
- Bengal Tiger: Found in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Bhutan, this species thrives in a variety of habitats, including forests and grasslands.
- Siberian Tiger: Also known as the Amur tiger, this species inhabits the cold forests of the Russian Far East.
- Sumatran Tiger: Native to the island of Sumatra, this species lives in tropical rainforests.
- Malayan Tiger: Found in the tropical forests of the Malay Peninsula, this species faces significant threats from habitat loss.
Tiger Adaptations to Their Habitats
Each tiger subspecies has unique adaptations that allow it to thrive in its specific habitat. For example:
Read also:Erik Lively The Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
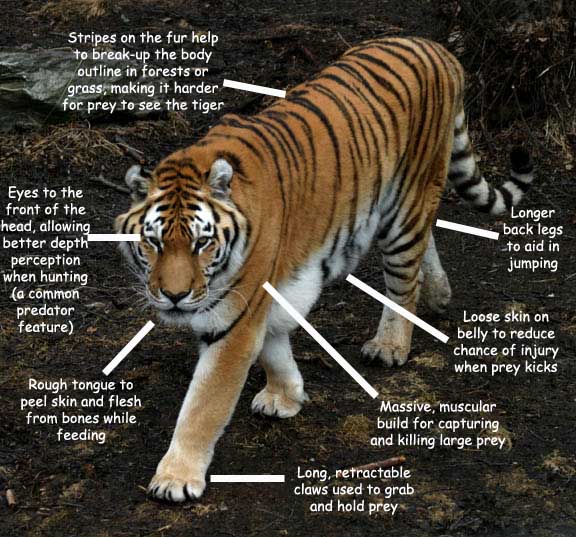
- Striped Coat: The tiger's distinctive coat provides camouflage, helping it blend into its surroundings.
- Powerful Build: Tigers have strong muscles and claws, enabling them to hunt efficiently in various terrains.
Threats to Tiger Habitats
Despite their adaptability, tigers face numerous threats to their habitats. Some of the most significant challenges include:
- Deforestation: The conversion of forests into agricultural land and urban areas reduces the available habitat for tigers.
- Poaching: Illegal hunting for tiger parts, such as bones and skins, continues to threaten their survival.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: As human populations expand, tigers are forced into closer proximity with people, leading to conflicts.
Impact of Habitat Fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation occurs when large, continuous habitats are divided into smaller, isolated patches. This phenomenon makes it difficult for tigers to find mates, hunt, and migrate. According to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), habitat fragmentation is one of the leading causes of tiger population decline.
Conservation Efforts for Tigers
Conservationists around the world are working tirelessly to protect tiger habitats and populations. Some of the most effective conservation efforts include:
- Tiger Reserves: Establishing protected areas where tigers can live without human interference.
- Anti-Poaching Measures: Implementing stricter laws and enforcement to combat illegal hunting.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts to reduce human-wildlife conflict.
Success Stories in Tiger Conservation
Several countries have reported success in their tiger conservation programs. For example:
- India: The country has seen a steady increase in tiger populations due to its robust conservation efforts.
- Russia: The Siberian tiger population has stabilized thanks to anti-poaching initiatives and habitat restoration.
Impact of Climate Change on Tiger Habitats
Climate change poses a significant threat to tiger habitats. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of natural disasters can alter ecosystems, making them less suitable for tigers. For example:
- Sea Level Rise: The Sunderbans, home to the Bengal tiger, is at risk of being submerged due to rising sea levels.
- Droughts and Floods: Extreme weather events can disrupt prey populations and reduce water availability.
Adapting to Climate Change
Conservationists are exploring ways to help tigers adapt to the changing climate. Strategies include:
- Habitat Restoration: Restoring degraded habitats to improve their resilience to climate change.
- Corridor Creation: Establishing corridors to connect fragmented habitats, allowing tigers to move freely.
Role of Human Activities in Tiger Habitat Loss
Human activities are the primary drivers of tiger habitat loss. Some of the most significant impacts include:
- Agricultural Expansion: Clearing forests for agriculture reduces the available habitat for tigers.
- Infrastructure Development: Roads, railways, and other infrastructure projects fragment habitats and increase human-wildlife conflict.
Sustainable Development Practices
Promoting sustainable development practices can help mitigate the negative impacts of human activities on tiger habitats. For example:
- Eco-Friendly Agriculture: Encouraging farming practices that minimize deforestation.
- Green Infrastructure: Designing infrastructure projects that consider wildlife corridors and habitats.
Interesting Facts About Tiger Habitats
Here are some fascinating facts about tiger habitats:
- Tigers are the largest of the big cats, with some individuals weighing over 600 pounds.
- The Siberian tiger can survive in temperatures as low as -40°C (-40°F).
- Tigers are solitary animals, with each individual requiring a large territory to hunt and live.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding where tigers live is crucial for their conservation and survival. Tigers inhabit a variety of ecosystems, from tropical rainforests to boreal forests, but their habitats are under threat from deforestation, poaching, and climate change. By implementing effective conservation strategies and promoting sustainable development practices, we can ensure that these magnificent animals continue to thrive in the wild.
We invite you to take action by sharing this article with your friends and family, supporting conservation organizations, and learning more about the world of tigers. Together, we can make a difference in protecting these iconic creatures and their habitats.