Quota rent is a term commonly used in international trade to describe the economic benefits derived from import quotas. It refers to the additional revenue or profit that arises when a government imposes a limit on the quantity of a particular good that can be imported. This concept plays a pivotal role in shaping trade policies, influencing market dynamics, and affecting the welfare of both producers and consumers. Understanding quota rent is essential for businesses, policymakers, and individuals who want to navigate the complexities of global trade.
As international trade continues to evolve, the concept of quota rent becomes increasingly relevant. Governments use import quotas as a tool to protect domestic industries, stabilize prices, and manage trade deficits. However, these measures often create economic distortions, leading to the emergence of quota rent. This article explores the intricacies of quota rent, its implications, and how it affects global trade.
This guide delves into the origins of quota rent, its calculation, and its broader implications for economic policy. Whether you're a student, researcher, or professional in the field of economics, this article provides valuable insights into one of the most significant aspects of international trade.
Read also:Where Is Hudsons Playground Farm Located Near
Table of Contents
- What is Quota Rent?
- History of Quota Rent
- How to Calculate Quota Rent
- Types of Quota Rent
- Impact of Quota Rent on the Economy
- Benefits and Challenges of Quota Rent
- Quota Rent and Trade Policies
- Real-World Examples of Quota Rent
- The Future of Quota Rent
- Conclusion
What is Quota Rent?
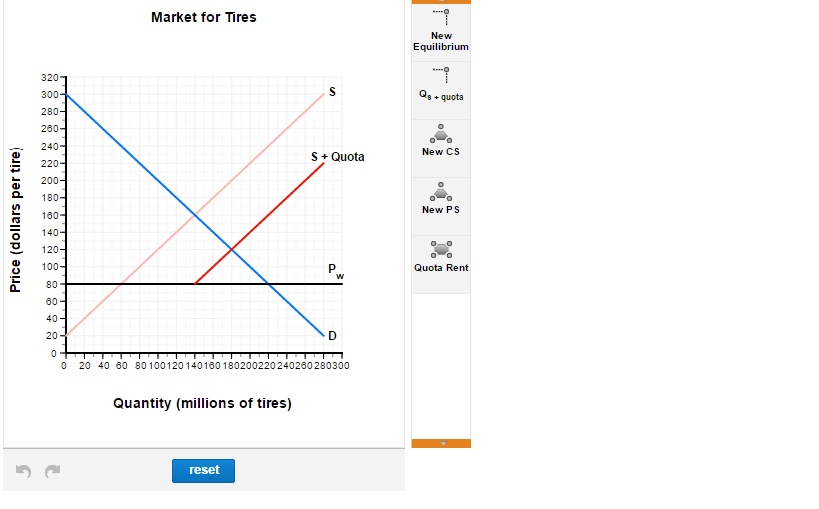
Quota rent refers to the additional revenue or profit generated due to the imposition of import quotas. When a government sets a limit on the quantity of a particular good that can be imported, it creates a situation where the price of that good in the domestic market increases. This price differential between the domestic and international markets leads to the creation of quota rent.
In essence, quota rent is the economic value derived from the limited supply of goods due to import quotas. It can be captured by various stakeholders, including governments, importers, and producers, depending on how the quota system is structured. Understanding this concept is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of international trade and the potential consequences of trade restrictions.
Key Features of Quota Rent
- Quota rent arises due to the artificial scarcity created by import quotas.
- It represents the difference between the domestic price and the world price of a good.
- The allocation of quota rent depends on the design of the quota system.
History of Quota Rent
The concept of quota rent has its roots in the early days of international trade. Historically, governments have used import quotas as a tool to protect domestic industries from foreign competition. The practice of imposing quotas dates back to the mercantilist era, where nations sought to accumulate wealth by controlling trade flows.
Over time, the understanding of quota rent evolved, with economists analyzing its implications for economic welfare. The modern interpretation of quota rent emerged in the 20th century, as global trade expanded and countries began negotiating trade agreements. These agreements often addressed the issue of import quotas and their associated economic effects.
Evolution of Quota Rent in Trade Policies
- Early use of quotas during the mercantilist era.
- Development of economic theories explaining quota rent in the 19th century.
- Incorporation of quota rent into international trade agreements in the 20th century.
How to Calculate Quota Rent
Calculating quota rent involves determining the difference between the domestic price and the world price of a good, multiplied by the quantity of the good imported under the quota. This calculation provides insight into the economic value generated by the quota system.
Formula: Quota Rent = (Domestic Price - World Price) × Quantity of Goods Imported Under Quota
Read also:Dana Reeves Death Date A Comprehensive Look At Her Life Legacy And Impact
This formula highlights the importance of understanding price differentials and the quantity of goods subject to quotas. Accurate calculation of quota rent is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of trade policies and assessing their impact on economic welfare.
Factors Affecting Quota Rent Calculation
- Domestic demand and supply conditions.
- World market prices for the good in question.
- The structure and enforcement of the quota system.
Types of Quota Rent
Quota rent can take various forms, depending on how the quota system is implemented. The most common types include:
Government-Collected Quota Rent
In some cases, governments collect quota rent by auctioning import licenses or charging fees for quota allocation. This approach ensures that the economic benefits of the quota system are captured by the state, which can then use the revenue for public purposes.
Importer-Captured Quota Rent
When import quotas are allocated directly to specific importers, these entities may capture the quota rent. This occurs when importers are able to sell the imported goods at higher domestic prices, thereby generating additional profits.
Producer-Captured Quota Rent
In certain scenarios, domestic producers may benefit from quota rent by charging higher prices for their goods. This happens when import quotas reduce competition from foreign producers, allowing domestic industries to increase their market share and profitability.
Impact of Quota Rent on the Economy
The introduction of quota rent can have both positive and negative effects on the economy. On one hand, it can protect domestic industries, stabilize prices, and generate revenue for the government. On the other hand, it can lead to inefficiencies, higher consumer prices, and reduced economic welfare.
Understanding the broader implications of quota rent is essential for policymakers and stakeholders involved in international trade. The economic impact of quota rent depends on factors such as the size of the quota, the nature of the goods being restricted, and the overall trade environment.
Economic Consequences of Quota Rent
- Protection of domestic industries from foreign competition.
- Increased prices for consumers, reducing purchasing power.
- Potential inefficiencies in resource allocation.
Benefits and Challenges of Quota Rent
While quota rent offers several benefits, it also presents significant challenges. One of the primary advantages is the ability to protect nascent or struggling domestic industries. By limiting imports, governments can provide a level playing field for local producers, enabling them to compete effectively in the global market.
However, the challenges associated with quota rent cannot be overlooked. These include the potential for corruption, rent-seeking behavior, and reduced consumer choice. Policymakers must carefully balance the benefits and drawbacks of quota rent to ensure that trade policies promote economic growth and welfare.
Key Benefits of Quota Rent
- Protection of domestic industries.
- Revenue generation for governments.
- Stabilization of prices in the domestic market.
Key Challenges of Quota Rent
- Potential for corruption and rent-seeking behavior.
- Higher prices for consumers.
- Reduced efficiency in resource allocation.
Quota Rent and Trade Policies
Quota rent plays a critical role in shaping trade policies around the world. Governments often use import quotas as part of their broader trade strategies, aiming to achieve specific economic and political objectives. The integration of quota rent into trade policies requires careful consideration of its potential impacts on various stakeholders.
International trade agreements, such as those negotiated through the World Trade Organization (WTO), often address the issue of import quotas and their associated economic effects. These agreements seek to promote fair trade practices while minimizing the distortions caused by quota rent.
Role of WTO in Managing Quota Rent
- Facilitating negotiations on import quotas.
- Providing a platform for resolving trade disputes related to quota rent.
- Encouraging transparency and accountability in quota allocation.
Real-World Examples of Quota Rent
Quota rent has been observed in various real-world scenarios, where governments have imposed import quotas to protect domestic industries. One notable example is the imposition of quotas on agricultural products, such as sugar and dairy, in many countries. These quotas have led to the creation of significant quota rent, benefiting domestic producers while increasing costs for consumers.
Another example is the use of quotas in the textile industry, where countries have limited the import of certain goods to support local manufacturing. These measures have generated substantial quota rent, influencing the competitiveness of domestic industries in the global market.
Case Study: Sugar Quotas in the United States
- The U.S. government imposes quotas on sugar imports to protect domestic producers.
- These quotas create substantial quota rent, benefiting domestic sugar producers.
- However, they also result in higher prices for consumers and reduced competitiveness for U.S. manufacturers that rely on sugar as an input.
The Future of Quota Rent
As global trade continues to evolve, the role of quota rent in shaping economic policies is likely to remain significant. Advances in technology, changes in consumer preferences, and shifts in geopolitical dynamics may influence the way governments use import quotas and manage quota rent.
Future developments in international trade agreements and global economic integration could lead to new approaches to addressing the challenges posed by quota rent. Policymakers will need to adapt to these changes while ensuring that trade policies promote sustainable economic growth and welfare.
Trends Shaping the Future of Quota Rent
- Increasing focus on digital trade and e-commerce.
- Growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations in trade policies.
- Advancements in technology and data analytics for monitoring and managing quota systems.
Conclusion
Quota rent is a critical concept in international trade, with far-reaching implications for economic policy and market dynamics. By understanding its origins, calculation, and impact, stakeholders can make informed decisions about trade policies and their potential effects on economic welfare.
In conclusion, quota rent plays a vital role in shaping the global trade landscape. While it offers benefits such as protecting domestic industries and generating revenue, it also presents challenges that require careful consideration. As the world continues to evolve, the role of quota rent in international trade will undoubtedly remain a topic of interest for policymakers, researchers, and businesses alike.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights on this article. Feel free to leave a comment or explore other articles on our site for more information on international trade and economic policy.