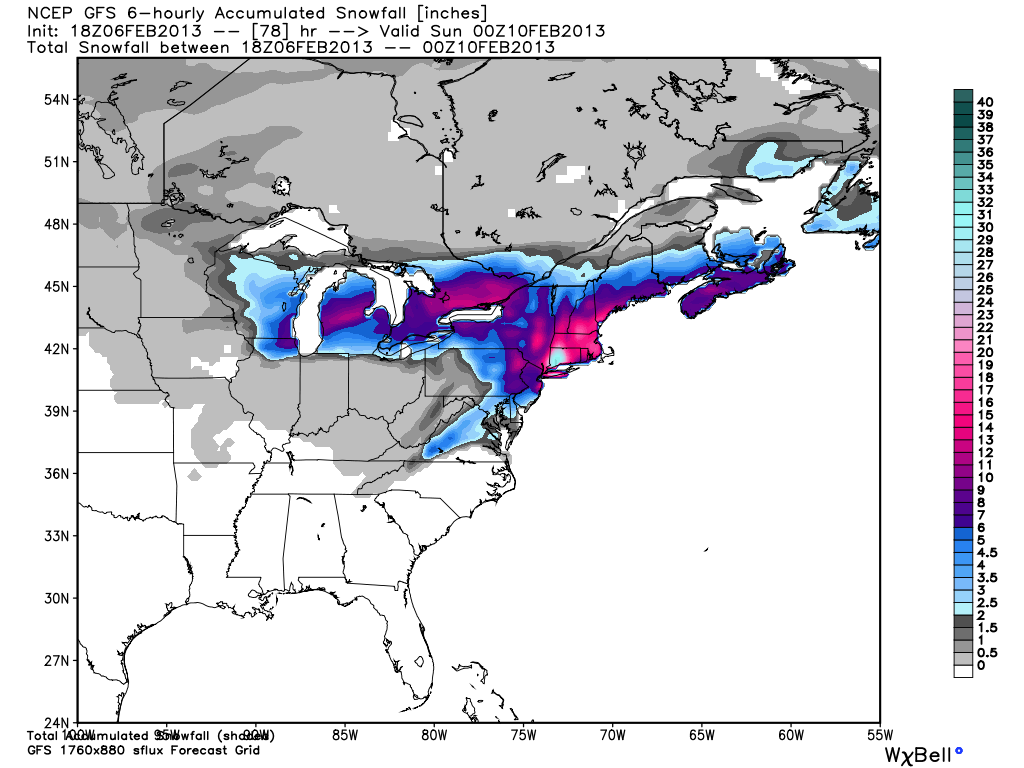
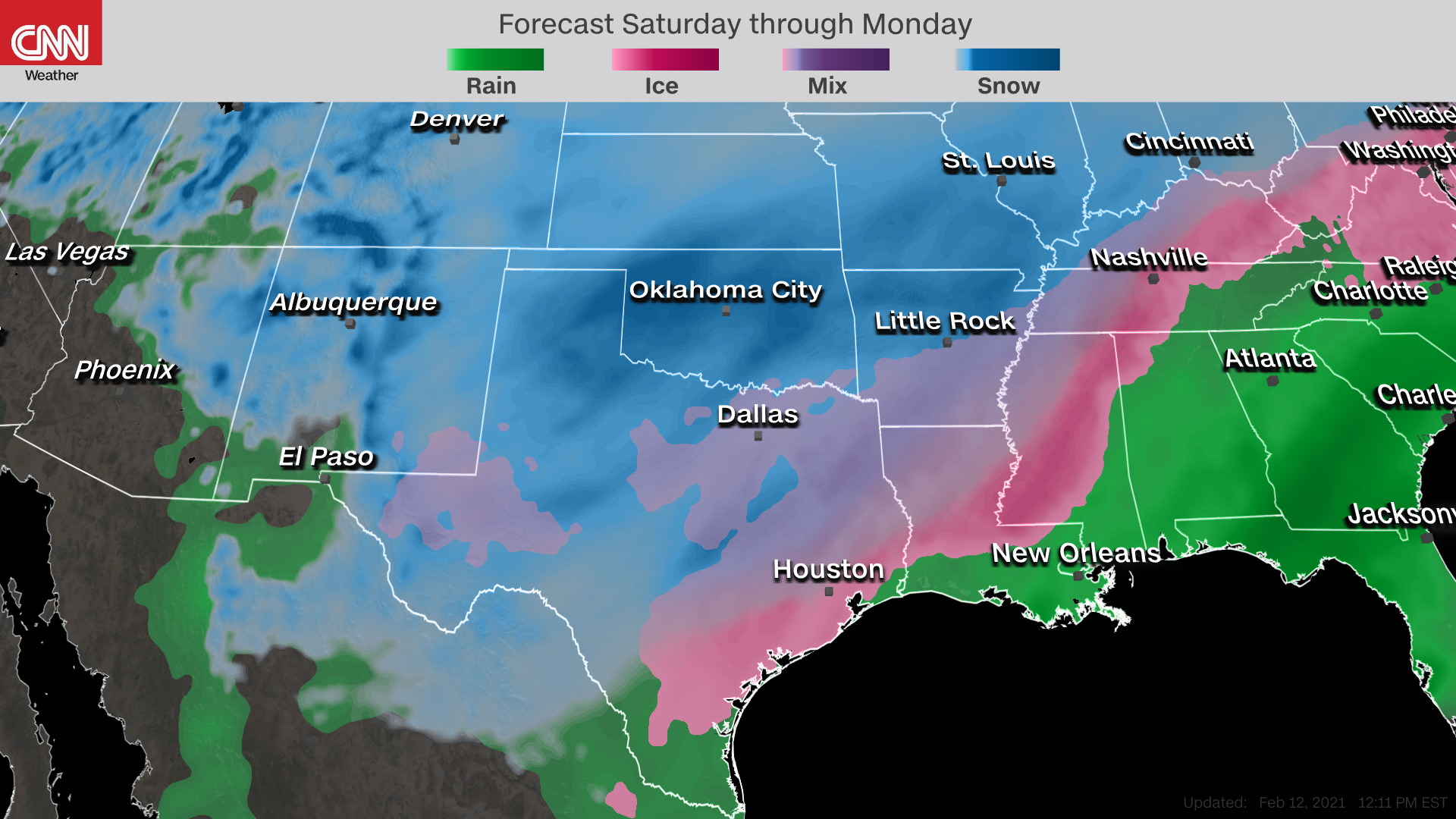
Winter weather forecasting plays a crucial role in ensuring public safety and efficient planning for communities across the globe. Snowfall prediction models are sophisticated tools that meteorologists use to anticipate snowfall intensity, timing, and location. These models have evolved significantly over the years, incorporating advanced technologies and vast amounts of data to provide more accurate forecasts. Whether you live in a snowy region or are simply curious about how these predictions are made, this article will delve into the intricacies of snowfall prediction models and their applications.
As climate patterns continue to shift, the accuracy of snowfall forecasts becomes even more critical. Businesses, governments, and individuals rely on these predictions to prepare for potential disruptions caused by heavy snowfall. From transportation systems to emergency services, accurate snowfall forecasts help mitigate risks and ensure safety during winter storms.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the science behind snowfall prediction models, their components, and their limitations. We'll also discuss the latest advancements in technology and how they contribute to improving forecast accuracy. By the end of this article, you'll have a deeper understanding of how meteorologists predict snowfall and why these models are essential for modern society.
Read also:Wentworth Miller Kids A Comprehensive Look Into The Personal Life Of The Renowned Actor
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Snowfall Prediction
- Types of Snowfall Prediction Models
- How Snowfall Prediction Models Work
- Key Components of Prediction Models
- Advantages and Limitations
- Accuracy of Snowfall Predictions
- Technology Advancements in Snowfall Prediction
- Case Studies: Real-World Applications
- The Future of Snowfall Prediction
- Conclusion
Introduction to Snowfall Prediction
Forecasting snowfall is a complex process that involves understanding atmospheric conditions, historical data, and real-time observations. Snowfall prediction models serve as the backbone of modern meteorology, providing critical insights into impending winter weather events. These models analyze various factors such as temperature, humidity, wind patterns, and atmospheric pressure to predict when and where snow will fall.
Historically, snowfall forecasting relied heavily on manual observations and basic calculations. However, with the advent of computer technology and satellite imagery, snowfall prediction models have become more sophisticated. Today, meteorologists use a combination of numerical weather prediction (NWP) models and machine learning algorithms to enhance forecast accuracy.
Why Snowfall Prediction Matters
The importance of snowfall prediction cannot be overstated. Accurate forecasts allow communities to prepare for potential disruptions, such as road closures, power outages, and school cancellations. Additionally, industries such as aviation, agriculture, and energy rely on snowfall predictions to optimize operations and minimize losses.
Types of Snowfall Prediction Models
Snowfall prediction models come in various forms, each with its strengths and limitations. The two primary categories are global models and regional models. Global models, such as the Global Forecast System (GFS), provide broad-scale predictions covering large geographical areas. Regional models, like the North American Mesoscale Model (NAM), focus on specific regions and offer higher resolution forecasts.
Global Models
- Global Forecast System (GFS): A widely used model that provides forecasts up to 16 days in advance.
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): Known for its high accuracy in medium-range predictions.
Regional Models
- North American Mesoscale Model (NAM): Offers detailed forecasts for North America with a focus on short-term weather events.
- Rapid Refresh (RAP): Provides high-frequency updates for short-term predictions.
How Snowfall Prediction Models Work
Snowfall prediction models operate by simulating the Earth's atmosphere using complex mathematical equations. These equations take into account variables such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. The models use initial conditions derived from real-time observations and historical data to generate forecasts.
One of the key processes in snowfall prediction is the analysis of precipitation types. Models must determine whether precipitation will fall as snow, rain, sleet, or freezing rain based on the temperature profile of the atmosphere. This involves analyzing the vertical temperature distribution and identifying the freezing level.
Read also:Conchita Martinez Partner A Comprehensive Look Into Her Relationships And Achievements
Key Components of Prediction Models
Several components contribute to the effectiveness of snowfall prediction models:
Data Inputs
Models rely on a vast array of data inputs, including:
- Satellite imagery
- Radar observations
- Surface weather stations
- Upper-air sounding data
Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
NWP is the foundation of modern snowfall prediction models. It involves solving mathematical equations that describe atmospheric behavior using powerful supercomputers. The accuracy of NWP models depends on the quality of initial data and the resolution of the model grid.
Machine Learning
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being integrated into snowfall prediction models to improve forecast accuracy. These algorithms analyze large datasets to identify patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent to human meteorologists.
Advantages and Limitations
While snowfall prediction models offer numerous benefits, they also have limitations that must be acknowledged.
Advantages
- Provide early warnings for impending snowstorms
- Enable better planning for emergency services
- Support industries affected by winter weather
Limitations
- Dependent on the quality and availability of input data
- Can struggle with sudden changes in atmospheric conditions
- May produce inaccurate forecasts in complex terrain
Accuracy of Snowfall Predictions
The accuracy of snowfall predictions has improved significantly over the years, thanks to advancements in technology and data collection. However, predicting snowfall remains a challenging task due to the inherent variability of atmospheric conditions. Studies have shown that models perform best when forecasting large-scale snow events, but accuracy decreases for localized or short-duration snowfalls.
According to research published in the Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, modern snowfall prediction models achieve an accuracy rate of approximately 80% for forecasts up to 48 hours in advance. Beyond this timeframe, accuracy diminishes due to the chaotic nature of weather systems.
Technology Advancements in Snowfall Prediction
Recent technological advancements have revolutionized the field of snowfall prediction. High-resolution satellite imagery, improved radar systems, and enhanced computational power have all contributed to more accurate forecasts. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has opened new possibilities for analyzing complex weather patterns.
Artificial Intelligence in Snowfall Prediction
AI algorithms are being used to analyze vast amounts of meteorological data and identify patterns that may not be immediately apparent to human forecasters. This has led to improvements in forecast accuracy, particularly for short-term predictions. Companies such as IBM and Google are actively developing AI-driven weather forecasting tools that promise even greater advancements in the future.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Several case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of snowfall prediction models in real-world scenarios. For example, during the 2010 "Snowmageddon" storm in the northeastern United States, the GFS and ECMWF models accurately predicted the storm's path and intensity several days in advance. This allowed local governments to prepare emergency response plans and minimize disruptions.
Another notable case is the 2018 "Beast from the East" storm in Europe, where regional models such as the UK Met Office's Unified Model provided critical warnings that helped save lives and reduce damage.
The Future of Snowfall Prediction
The future of snowfall prediction looks promising, with ongoing research and development in several key areas. Improved data collection methods, enhanced computational capabilities, and the continued integration of AI and machine learning will likely lead to even more accurate forecasts. Additionally, advancements in climate modeling may help meteorologists better understand how climate change will impact snowfall patterns in the future.
Conclusion
Snowfall prediction models are indispensable tools for modern meteorology, providing critical insights into winter weather events. From global models to regional systems, these models have evolved significantly over the years, incorporating advanced technologies and vast amounts of data to improve forecast accuracy. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in technology and data analysis promise even greater improvements in the future.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with snowfall prediction in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on weather forecasting and related topics. Together, we can stay informed and prepared for whatever winter weather may bring.